751.10 General Superstructure
751.10.1 Slab on Girder
751.10.1.1 Material Properties
| Concrete | ||
|---|---|---|
| Unit weight of reinforced concrete, | = 150 | |
| Concrete Slab on Girders shall consist of: | ||
| Class B-2 Concrete | = 4.0 ksi | |
| = 8 | ||
| Concrete modulus of elasticity, | = 33000 | |
| Where: | ||
| = Unit weight of non-reinforced concrete = 0.145 kcf | ||
| Modulus of rupture: | ||
| For minimum reinforcement, | = 0.37 | |
| For deflection, camber and | ||
| distribution reinforcement | = 0.24 | |
| Safety Barrier Curbs | ||
| Safety Barrier Curbs shall consist of: | ||
| Class B-1 Concrete | = 4.0 ksi | |
| = 8 | ||
| Median Barrier Curbs | ||
| Median Barrier Curbs shall consist of: | ||
| Class B-1 Concrete | = 4.0 ksi | |
| = 8 | ||
| Future Wearing Surface | ||
| Unit weight of future wearing surface, | = 140 | |
| Reinforcing steel | ||
| Minimum yield strength, | = 60.0 ksi | |
| Steel modulus of elasticity | = 29000 ksi | |
751.10.1.2 Limit States and Load Factors
In general, each component shall satisfy the following equation:
Where:
| = Total factored force effect | |
| = Force effect | |
| = Load modifier | |
| = Load factor | |
| = Resistance factor | |
| = Nominal resistance | |
| = Factored resistance |
Limit States
The following limit states shall be considered for slab interior and overhang design:
| For slab interior design: | STRENGTH – I<br\>SERVICE – I* |
| For slab overhang design: | EXTREME EVENT – II<br\>STRENGTH – I<br\>SERVICE – I* |
| *Of deformation, cracking, and concrete stresses, only cracking<br\>need be considered here. | |
| FATIGUE limit state need not be investigated for concrete decks<br\>in multi-girder bridges due to observed performance and laboratory<br\>testing. | |
Resistance factors
For STRENGTH limit state,
- Flexure and tension of reinforced concrete, = 0.90
- Shear and torsion, = 0.90
For all other limit states, = 1.00
751.10.1.3 Loads
Permanent (Dead) Loads
Permanent loads include the following:
- Slab weight
- Future Wearing Surface
- A 3” thick future wearing surface (35psf) shall be considered on the roadway.
- Safety Barrier Curb (SBC)
- For slab overhang design, assume the weight of the SBC acts at the centroid of the SBC.

(*) 12" for slab design (LRFD (3.6.1.3.1), 2'-0" for other design
Application of Live Load to Slab
Gravity Live Loads<br\>
Gravity live loads include vehicular, dynamic load allowance, and pedestrian loads.
- Vehicular
- The design vehicular live load HL-93 shall be used. It consists of either the design truck or a combination of design truck and design lane load.
- For slab design, where the equivalent strip method is used, the force effects shall be determined on the following basis:
- Where primary strips are transverse the design shall be based on the truck alone.
- Where primary strips are transverse and their span exceeds 15 ft – the design shall be based on the truck and lane load. For the purpose of slab design, the lane load consists of a load equal to 64 psf uniformly distributed over 10 feet in the transverse direction.
Dynamic Load Allowance<br\>
The dynamic load allowance replaces the effect of impact used in AASHTO Standard Specifications. It accounts for wheel load impact from moving vehicles. For slabs, the static effect of the vehicle live load shall be increased by the percentage specified in Table below.
| Slab Component | IM |
|---|---|
| Deck Joints – All Limit States | 75% |
| All Other Limit States | 33% |
The factor to be applied to the static load shall be taken as:
The dynamic load allowance is not to be applied to pedestrian or design lane loads.
Multiple Presence Factor, m:
The multiple presence factor accounts for the probability for multiple trucks passing over a multilane bridge simultaneously.
| m = | 1.20 for 1 Loaded Lane |
| 1.00 for 2 Loaded Lanes | |
| 0.85 for 3 Loaded Lanes | |
| 0.65 for more than 3 Loaded Lanes |
Pedestrian
Pedestrian live load on sidewalks greater than 2 ft wide shall be:
| PL = | 0.075 ksf |
This does not include bridges designed exclusively for pedestrians or bicycles.
Collision Loads
Collision loads applied to the safety barrier curb (SBC) shall be transferred to the slab overhang. The design forces from SBC consist of lateral and vertical components that are to be considered separately. Because of MoDOT’s experience with the collision survivability of bridge decks that utilize the standard barriers, MoDOT does not require the deck overhang to be designed for forces in excess of those resulting from the design loads for Traffic Railings shown in LRFD Table A13.2-1. The standard slab crosssections reflect this design philosophy.
- Design Case 1
- The collision force and moment shall be considered.
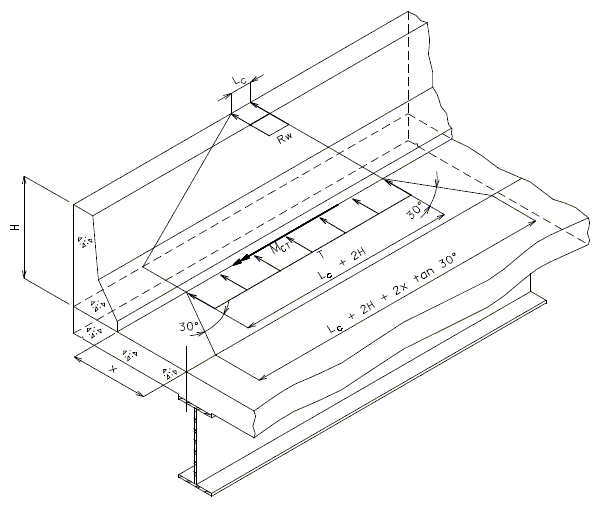
- Slab Overhang Design Collision Moment
- The design collision moment at the base of the curb is the barrier curb moment capacity about the curb longitudinal axis. For SBC design with either failure mechanism 1 or 2 controlling:
- (averaged over height of SBC)
- Slab Overhang Design Collision Force
- A refined analysis may be preformed. In this case the design collision moment at the base of the curb, Mct, is to be taken as the average moment over the theoretical distribution length (Lc+2H for continuous sections), when the TL-4 collision load is applied to the top of the curb.
- For continuous sections of safety barrier curbs:
- Where:
= total transverse resistance of curb (k) = critical length of yield line failure pattern (ft) = height of curb (ft) = tensile force per unit of deck length at base of curb (k/ft)
- For discontinuous safety barrier curb sections:

Transfer of Safety Barrier Curb Collision Forces
Transfer of Safety Barrier Curb Collision Forces751.10.1.4 Design and Analysis Methods
Equivalent Strip Method
The equivalent strip method is an approximate method of analysis in which the reinforcing steel is designed using a certain width of deck to resist the applied loading. Where the strip method is used, the extreme positive moment in any slab section between girders shall be taken to apply to all positive moment regions, and similarly with extreme negative moments.
There are other methods of analysis allowed, such as finite element method, but the equivalent strip method is recommended.
751.10.1.5 Interior Section Design
Slab Thickness
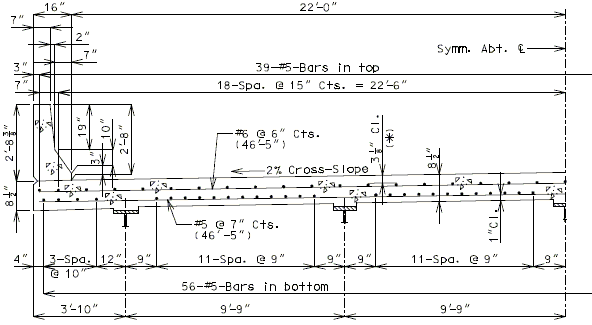
The slab portion between girders shall be 8 1/2” thick for both the full depth cast-in-place (CIP) concrete and partial depth precast prestressed (P/C P/S) concrete panel standard slabs.
Design Cases
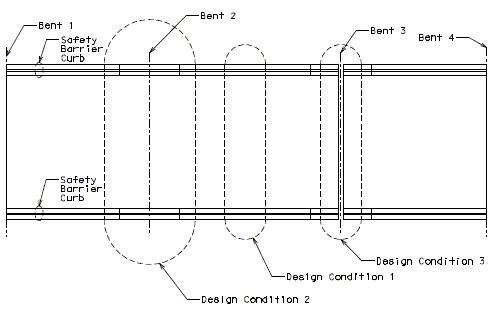
Two design cases shall be considered for each design condition.
Design Case 1 STRENGTH I load combination for reinforcing design.
Design Case 2 SERVICE I load combination for cracking check.
Design Conditions
Two design conditions can exist for the slab interior.
Design Condition 1 – Continuous Slab, where the slab section under consideration is not near an end bent or expansion joint.
Design Condition 2 – Discontinuous Slab, where the slab section under consideration is at an end bent or expansion joint.
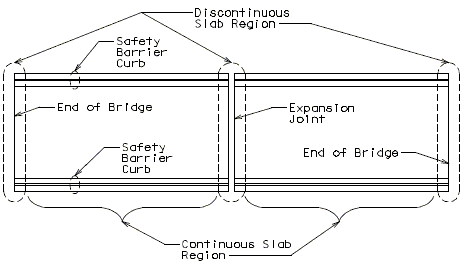
Critical Sections
The critical design section for negative moments may be taken as follows:
| For steel girders - | the design negative moment should be taken at<br\>1/4 of the flange width from the centerline of the web. |
| For P/S-I girders - | the design negative moment should be taken at 1/3<br\>of the flange width, but not exceeding 15” from the<br\>centerline of the web |
The critical design slab section for positive moment shall be taken at location of maximum positive moment – generally midway between girders.
Width of Equivalent Strip at Continuous Slab Section
| For Positive Moment | |
| For Negative Moment |
Where:
| = equivalent strip width (in) | |
| = spacing of centerline to centerline of supporting components (ft) |
Width of Equivalent Strip at Discontinuous Slab Section
The effective strip width shall be taken as ½ of the equivalent strip width for a continuous slab section plus the distance between the transverse edge of slab and the edge beam (if any).

Determining Live Load
Slab interior live load design moments may be determined using Appendix Table A4-1 of the LRFD Specifications, provided that the assumptions used in the table are appropriate. It is assumed that the table is only applicable to continuous sections of slab (not at joints). It may be used at discontinuous sections by adjusting the tabulated moments as follows:
Where:
| = equivalent strip width (in). | |
| = vehicular dynamic load allowance. |
Note: includes multiple presence factor, .
Alternatively, the designer may use other sources to determine the design moments. For example any capable computer program for finite element design may be used.
The general methodology for applying live load to slab on girder with transverse primary strips is:
- Model the bridge cross section.
- Define the design vehicle (design truck).
- Move the design vehicle between the barrier curbs and add additional design vehicles as required to produce the maximum force effect. The wheel load shall not be closer than 1 ft. to the face of safety barrier curb and wheel loads of adjacent design vehicles shall not be closer than 4 ft. The design lane is assumed to occupy a 10 ft. width. Partial trucks (i.e. one wheel) should not be used.
Determining Dead Load
Although P/C P/S panel slab is the preferred slab used for construction (when allowed), it may be assumed for slab analysis that slab is cast-in-place (CIP). The maximum negative and positive dead load moment may be taken to be:
Continuous over 4 girders (equally spaced):
Continuous over 5 girders (equally spaced):
Where:
| = moment at centerline of exterior girder due to: slab, future wearing surface, SBC, sidewalk, and other dead load components | |
| = center-to-center girder spacing |
Determining Top Reinforcing
The top (negative) reinforcing steel may be determined by assuming the section to be either singly- or doubly-reinforced, as needed.
Determining Bottom Reinforcing
The bottom (positive) reinforcing steel may be determined by assuming the section to be either singly- or doubly-reinforced, as needed. A 1” wearing surface shall be removed from the effective depth, .
Minimum Limit of Reinforcement
The amount of tension reinforcement shall be adequate to develop a factored flexural resistance, , a least equal to the lesser of either:
- 1.2 times the cracking strength determined on the basis of elastic stress distribution and the modulus of rupture, , of the concrete.
- 1.33 times the factored moment required by the applicable strength load combinations specified in LRFD Table 3.4.1-1
Shrinkage and Temperature Reinforcement
The area of reinforcing for top longitudinal steel, As, shall not be less than:
Where:
| = area of top longitudinal reinforcement | |
| = gross area of slab section (in^2) |
Maximum spacing of longitudinal reinforcement =
- 5 @ 15” are shown for standard slabs.
Distribution Reinforcement
The bottom longitudinal steel, as a percentage of the bottom primary reinforcement, shall not be less than:
Where:
| = effective span length (ft) specified in LRFD 9.7.2.3. It is the distance between flange tips, plus the flange overhang, taken as the distance from extreme flange tip to the face of the web. |

Concrete Cover
Existing (pre-LRFD) MoDOT concrete cover requirements for bridge slabs will be retained here. The cover requirements that follow meet or exceed LRFD requirements.
| At Bottom of CIP slabs | 1.00 in |
| Bottom of CIP slab over P/C P/S panels | 1.00 in |
| Top reinforcing | 3.00 in preferred |
| 2.75 in absolute min. |
Spacing Limits
LRFD 5.10.3.1.1 Minimum clear spacing between parallel bars in a layer:
| Maximum of: | 1) 1.5 where is bar diameter (in) |
| 2) 1.5 times maximum aggregate size (*) | |
| 3) 1.5 in |
(*) see Missouri Standard Specifications for Highway Construction
Bar Development
The calculated force effects in reinforcement shall be developed on each side of the critical section.
Cracking Check
Actual Stress
A transformed cracked section analysis shall be used with SERVICE-I moments to determine actual stress in reinforcing.
The spacing of mild steel reinforcement in the layer closest to the tension face shall satisfy the following:
in which:
Where:
| = exposure factor | |
| = .75 for class 2 exposure condition. | |
| = actual thickness of concrete cover measured from extreme tension fiber to center of the flexural reinforcement located closest thereto (in) | |
| = tensile stress in steel reinforcement at the service limit state (ksi) |
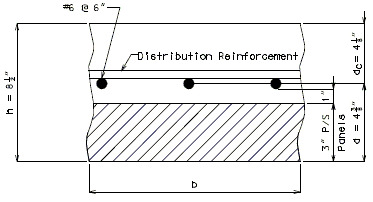
Reinforcing Placement
Although LRFD Specifications allow slab primary reinforcing to be skewed with the bridge under certain cases, MoDOT Bridge practice is to place transverse reinforcing perpendicular to roadway
Note: Due to the depth of cover and location of primary reinforcement, the cracking check shown on the previous page does not appear to be accurate for Missouri’s bridge decks shown above.
Negative Moment Steel over Intermediate Supports
Dimension negative moment steel over intermediate supports as shown.
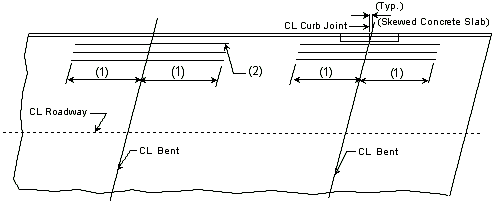
| (1) | Bar length by design | |
| (2) | Reinforcement placed between longitudinal temperature reinforcing in top. | |
| Bar size: | #5 bars at 7 1/2" cts. (Min.) | |
| #8 bars at 5" cts. (Max.) | ||
Steel Structures:
| (1) | Extend into positive moment region beyond "Anchor" Stud shear connectors at least 40 x bar diameter x 1.5 (Epoxy Coated Factor) (*) as shown below. |
| (2) | Use #6 bars at 5" cts. between longitudinal temperature reinforcing in top. |
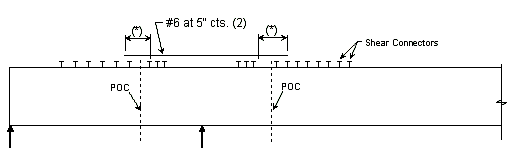
Locations of termination of reinforcement steel in the deck slab for Prestressed Structures shall be checked for the following criteria and adjusted as necessary:
- No more than 50 percent of the reinforcement shall be terminated at any section.
- Adjacent bars shall not be terminated in the same section.
- Flexural reinforcement shall be extended beyond the point at which it is no longer required to resist flexure for a distance not less than:
- The effective depth of the member
- 15 times the nominal diameter of bar
- 1/20 of the clear span (centerline to centerline of pier)
- Continuing reinforcement shall extend not less than the development length, ld, beyond the point where reinforcement is no longer required to resist flexure.
- At least one third of the total tension reinforcement provided for negative moment at a support shall have an embedment length beyond the point of inflection not less than:
- The effective depth of the member
- 12 times the nominal diameter of bar
- 0.0625 times the clear span (centerline to centerline of pier)
751.10.1.6 Slab Overhang Section Design
Girder Layout
In order to use distribution factors provided in LRFD Table 4.6.2.2.2 for girder design, the roadway overhang shall not exceed 5.5 ft.
Slab Thickness
The slab overhang shall be 8 1/2” slab thickness.
Design Cases
Four design cases shall be considered for each design condition.
| Design Case 1 | EXTREME EVENT II load combination with transverse and longitudinal collision force components |
| Design Case 2 | EXTREME EVENT II load combination with vertical collision force components (Does not control slab for TL-4). |
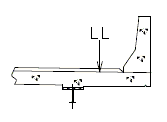
| Design Case 3 | STRENGTH I load combination |
| Design Case 4 | SERVICE I load combination for cracking check |
Design Conditions
Three design conditions may exist for slab overhang design.
| Design Condition 1 – | Continuous Slab & Continuous SB |
| Design Condition 2 – | Continuous Slab & Discontinuous SBC |
| Design Condition 3 – | Discontinuous Slab & Discontinuous SBC |
Critical Sections
The critical design section for slab overhang shall be at the following two locations:
- At roadway face of safety barrier curb
- At exterior girder:
- For steel girders – the design negative moment should be taken at ¼ of the flange width from the centerline of the web.
- For P/S-I girders - the design negative moment should be taken at 1/3 of the flange width, but not exceeding 15” from the centerline of the web.
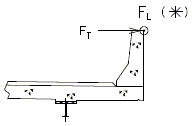
|
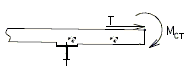
|
| SBC Loading | Slab Design Loading |
| DESIGN CASE 1 | |
|---|---|
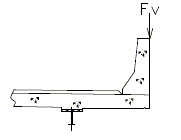
| |
| DESIGN CASE 2 | |
| |
| LL = vehicular live load | |
| DESIGN CASE 3 | |
Width of Equivalent Strip at Continuous Slab Section
The equivalent strip width for a continuous section of slab overhang shall be:
Where:
| = equivalent width (in) | |
| = distance from load to point of support (ft) |
Width of Equivalent Strip at Discontinuous Slab Section
LRFD 4.6.2.1.4c The effective strip width shall be taken as 1/2 of the equivalent strip width for a continuous slab section plus the distance between the transverse edge of slab and the edge beam (if any). This shall not be taken to be greater than equivalent strip width for continuous slab section.
Assumed Load Distribution
To determine the load effect at slab overhang critical sections, the slab shall be assumed as fixed at the exterior girder. This assumption is intended for slab design only, not the distribution of slab loads to girder.
For the purpose of determining the collision load effect at slab critical sections, the load may be assumed to fan out at 30 degrees on each side from the point of load.
Determining Top Reinforcing
The top (negative) reinforcing steel may be determined by assuming the section to be either singly- or doubly-reinforced, as needed. For slab overhang lengths equal to or less than 3’-10”, the reinforcement shown in the standard slab details is adequate (see EPG 751.10.1.7). For overhang lengths greater than 3’-10”, further analysis is required for top transverse steel design.
Effect of Slab Drains
The effect of slab drain openings in the slab overhang shall be considered. Their effect may be considered by ensuring the following:
Where:
| = area of steel provided over the strip width including effect of drain openings | |
| = area of steel required over strip width by calculation |
Reinforcing Criteria
Reinforcing limits, cover, temperature steel, distribution steel, and placement shall be the same as for Slab Interior Section.
Special Considerations for SBC-Mounted Light Pole
Standard details for mounting 30 ft. and 45 ft. Type B light poles on safety barrier bridge curb are provided. At the barrier curb-to-slab interface, the force effect of wind on the light pole (STRENGTH - III) with 90 m.p.h. wind is less than that due to EXTREME EVENT-II (TL-4) on safety barrier bridge curb. Therefore, reinforcing designed for EXTREME EVENT-II (TL-4) load combination will be adequate.
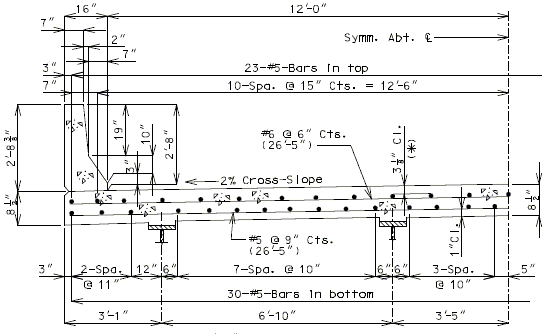
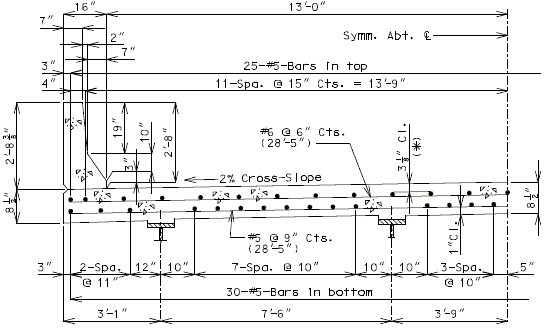
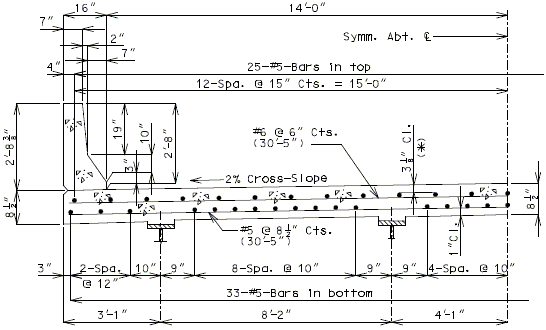
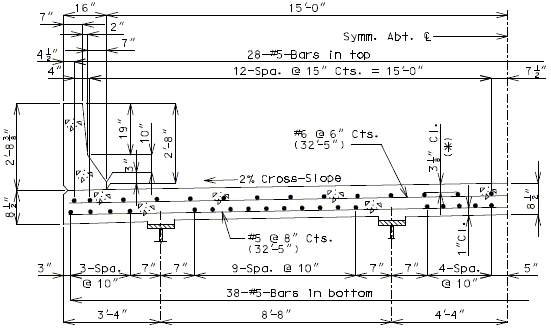
751.10.1.7 Standard Slab Details
751.10.1.7.1 Standard Full Depth CIP Slab Details Using Conventional Forms
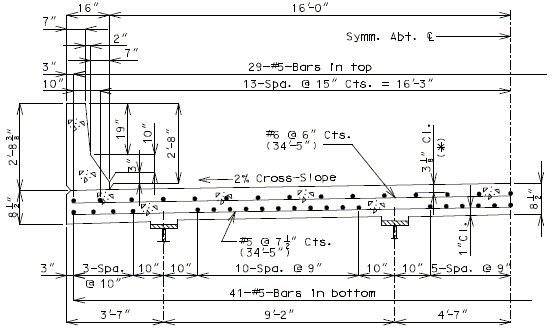
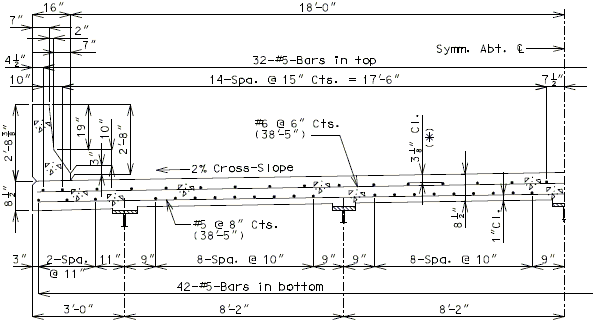
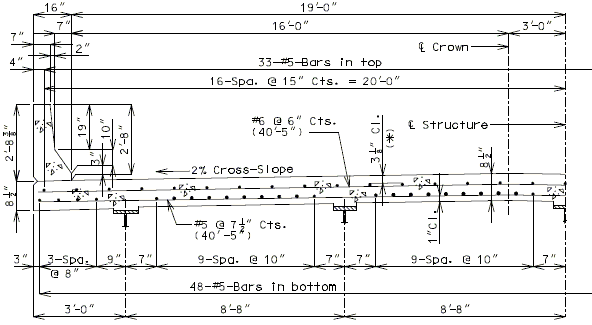
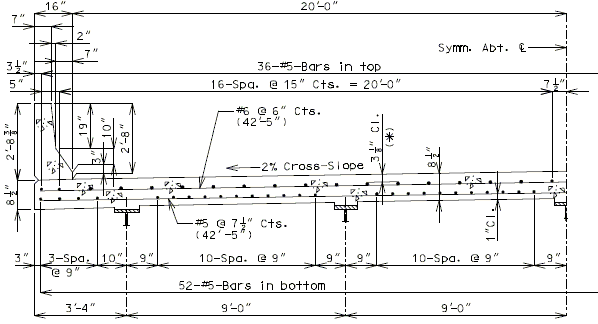
| ( A ) | Full depth cast-in-place concrete (CIP) slab cross sections and slab reinforcement designed for the HL-93 live load are shown for nine standard roadway widths. |
| ( B ) | Slab design includes an allowance for 35 psf future wearing surface. |
| ( C ) | Slab design is based on ultimate strength design, f’c = 4 ksi, and grade 60 reinforcing steel. |
| ( D ) | When the flange width exceeds the bottom longitudinal reinforcement spacing over the girder, reduce the bar spacing between the girders and increase the bar spacing over the girder to clear the flange edges. |
| ( E ) | When the structure is on grade, determine lengths of the longitudinal reinforcement in the slab and safety barrier curb from the actual length. |
| ( F ) | For slab design, the centerline of wheels is located 1 foot from face of barrier or curbs. |
| ( G ) | Standard slabs were designed assuming 12” minimum flanges and are applicable for plate girders, wide flange beams, MoDOT prestressed girders, and NU and bulb-tee girders when slab drains are not required or slab cantilevers that are less than 3’-8” in the case of bulb-tee girders. |
| ( H ) | The bridge roadway width, from gutter line to gutter line, shall be the same as the roadway width (from outside edge of shoulder to outside edge of shoulder). |
| ( I ) | Standard slab designs do not include the effect of features not shown (i.e. sidewalk, fence, utilities, etc…) except for future wearing surface. |
| ( J ) | Minimum concrete cover for slab top bars is 2 ¾” (*) for #8 longitudinal bars. |
| (K) | The standard slab reinforcements shown in this article for HL-93 live load were designed using stay-in-place (SIP) dead loads given in EPG 751.10.2.3. |
| Note: | Generally, when the deck is bid in sq. yd., curbs are bid in linear ft., and when the deck is bid in cu. yd., curbs are bid in cu. yd. |
| (*) Cover will be less for greater than #5 longitudinal bars. |
751.10.1.7.2 Standard Partial Depth P/C P/S Panel Slab Details Using SIP Forms
| (A ) | Partial depth precast prestressed (P/C P/S) concrete panel slab cross sections are not shown. The 3” precast prestressed (P/C P/S) concrete panel forms with 5½” minimum cast-in-place concrete shall be the preferred slab used on all girder superstructures except as noted in 751.10.2.1. For details, use CIP slab cross sections and top slab reinforcement only replacing the bottom layer of reinforcement between the girders with P/C P/S panels. Cantilever reinforcement details for P/C P/S panel slab are shown in EPG 751.10.2.2. |
| ( B ) | Slab design includes an allowance for 35 psf future wearing surface. |
| ( C ) | Slab design is based on ultimate strength design, f’c = 4 ksi and grade 60 reinforcing steel for cast-in-place concrete and EPG 751.10.2.1 for P/C P/S panel form design. |
| ( D ) | Haunching diagrams shall be provided for only the P/C P/S panel slab. Quantities for slab haunching may be estimated by taking 4% of slab quantities for steel structures and 2% for prestressed structures. More exact methods are recommended. |
| ( E ) | When the structure is on grade, determine lengths of the longitudinal reinforcement in the slab and safety barrier curb from the actual length. |
| ( F ) | For slab design, the centerline of wheels is located 1 foot from face of barrier or curbs. |
| ( G ) | Standard slabs were designed assuming 12” minimum flanges and are applicable for plate girders, wide flange beams, MoDOT prestressed girders, and NU and bulb-tee girders when slab drains are not required or slab cantilevers that are less than 3’-8” in the case of bulb-tee girders. |
| ( H) | When a safety barrier curb or median barrier curb is permanently required on the structure, other than at the edge of slab or where P/C P/S panels are not used for other reasons, P/C P/S panels shall not be used in the bay underneath the barrier. Check reinforcement in the CIP bay for collision and wheel loads on opposite faces of the barrier and provide suitable anchorage of the barrier reinforcing steel. |
| ( J ) | The bridge roadway width, from gutter line to gutter line, shall be the same as the roadway width (from outside edge of shoulder to outside edge of shoulder). |
| ( K ) | The P/C P/S panels shall be used in at least two adjacent bays. |
| ( L ) | Standard slab designs do not include the effect of features not shown (i.e. sidewalk, fence, utilities, etc…) except for future wearing surface. |
| (M) | Minimum concrete cover for slab top bars is 2 ¾” (*) for #8 longitudinal bars. |
| Note: | Generally, when the deck is bid in sq. yd., curbs are bid in linear ft., and when the deck is bid in cu. yd., curbs are bid in cu. yd. |
| (*) Cover will be less for greater than #5 longitudinal bars. |
751.10.1.8 Epoxy Coated Reinforcement
GENERAL
All reinforcement in the slab and above, and all reinforcement that extends into the slab, shall be epoxy coated; also, any wing reinforcement that extends into the safety barrier curb shall be epoxy coated.
NON-INTEGRAL END BENTS WITH EXPANSION DEVICES
The #6 bars in the end bent backwall above the upper construction joint shall be epoxy coated. V-bars in the backwall shall also be epoxy coated.

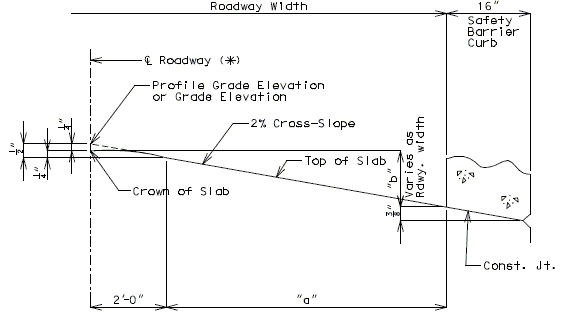
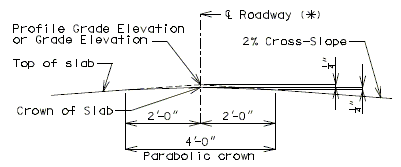
751.10.1.9 Standard Parabolic Crown
Use parabolic rounding for all bridges at the crown of the roadway except for the bridges with superelevated slabs. The profile grade will be at the intersection of the two cross-slopes if it is located at the crown of the roadway.
751.10.1.10 Profile Grade & Vertical Curve Data
PROFILE GRADE
See the Design Layout for location of the profile grade.
Generally, the profile grade is at the centerline of roadway for two-way traffic bridges.
For one-way traffic bridges (as used in standard divided highways), the profile grade is at some other location away from the centerline of roadway.
Generally, the profile grade will be shown in the cross section through the superstructure on the slab sheet and in the plan view on the front sheet of the design plans.
Show stations and profile grade elevations for all bents in the plan view on the front sheet of the design plans.

VERTICAL CURVE DATA
Place the vertical curve data on the front sheet near the elevation view at the vertical curve P.I. station, or as near to the vertical curve P.I. station as practical.

A crest vertical curve detail is shown. If the bridge is located on a sag vertical curve, then the detail for a sag vertical curve is to be used.
751.10.1.11 Slab Elevations
Slab elevations are used to determine haunching at the tenth points of steel and prestressed girder spans over seventy-five feet in length. Spans less than seventy-five feet in length use quarter points.
Theoretical Bottom of Slab Elevations at Centerline of Girder (Prior to Forming for Slab)
Elevations and details for Theoretical Bottom of Slab Elevations at Centerline of girder (prior to forming for slab) shall be provided on all stringer or girder type structures.
Steel Girders
Elevations are determined by adding DL1 and DL2 deflections to finished bottom of slab elevations. DL1 deflections are reduced by the percent of dead load deflection due to the weight of structural steel. DL2 deflections are reduced by the percent of dead load deflection due to future wearing surface.
P/S I-Girders
Initial camber minus final camber is used to determine DL1 deflection.

- (**) Elevations are based on a constant slab thickness of 8 1/2" and include allowance for theoretical
dead load deflections due to weight of Slab (including Prestressed Panel) and Barrier Curb.
- (**) Elevations are based on a constant slab thickness of 8 1/2" and include allowance for theoretical

| Example: | |
|---|---|
| 972.0715 | Finished top of Slab Elevation at centerline of girder |
| - 0.7083 | Slab Thickness |
| 971.3632 | Finished Bottom of Slab Elevation at centerline of girder |
| + 0.0478 | Theoretical Dead Load Deflection due to weight of slab and barrier curb. |
| 971.4110 | Theoretical Bottom of Slab Elevation at centerline Girder (Prior to Forming for Slab) |
| 971.41 | (USE) Theoretical Bottom of Slab Elevation at centerline Girder (Prior to Forming for Slab) |
and
Simple Span Plate Girder and Wide Flange Girder Design and Details

- (**) Elevations are based on a constant slab thickness of 8 1/2" and include allowance for theoretical
dead load deflections due to weight of Slab (including Prestressed Panel) and Barrier Curb.
- (**) Elevations are based on a constant slab thickness of 8 1/2" and include allowance for theoretical

| Example: | |
|---|---|
| 830.7504 | Finished top of Slab Elevation at centerline of girder |
| - 0.7083 | Slab Thickness |
| 830.0421 | Finished Bottom of Slab Elevation at centerline of girder |
| + 0.1348 | Theoretical Dead Load Deflection due to weight of slab and barrier curb. |
| 830.1769 | Theoretical Bottom of Slab Elevation at centerline Girder (Prior to Forming for Slab) |
| 830.18 | (USE) Theoretical Bottom of Slab Elevation at centerline Girder (Prior to Forming for Slab) |
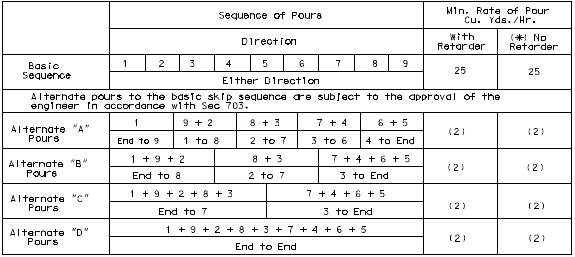
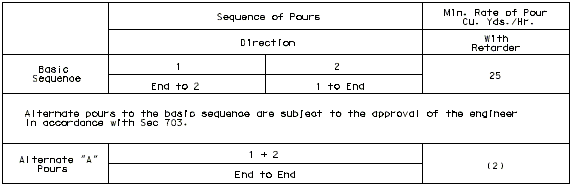
751.10.1.12 Slab Pouring Sequences
Concrete pouring and finishing with/without rates are based on the following:
One pouring sequence must be provided that will permit a minimum pouring rate of 25 cubic yards per hour without retarder for steel structures and with retarder for prestressed structures. A minimum finishing rate of 20 linear feet per hour is also required. If these two requirements conflict, see the Structural Project Manager.
Continuous steel structures will normally require a case I pouring sequence with the basic sequence being a skip pour arrangement. Minimum yardage for the basic sequence shall not be less than 25 cubic yards per hour. Computation of minimum yardage for alternate pours is outlined below. If the rate for the alternate pours should be 25 yards or less, the skip pour basic sequence may be eliminated with the first alternate pour becoming the basic sequence.
Use of retarder is required for prestressed structures and a case II sequence * is normally required. The minimum rate of pour will be determined by the 20 feet per hour minimum finishing rate but shall not be less than 25 cubic yards per hour. For span lengths over 80'or special structures (segmental, etc.), see Structural Project Manager.
- = Slab width (out to out of curbs, or width being poured)(ft.)
- = 8 1/2" (slab thickness)
- = Volume of concrete (cu. yds./hr.)
- (two span) = Length of longest alternate "A" pour (ft.)
- (more than two span) = Length of longest span (ft.)
(*) Case II sequence is used for all prestressed structures, except if slab area of one span is greater than 3,000 sq. ft., use case I.
Minimum rate of pour/hour for alternate pours (reduce V by 25% for P/C P/S Panels).
| Without Retarder: | |
|---|---|
| Not less than | |
| With Retarder: | |
| Not less than | |
| Simple Span: | |
| Not less than | |
Extra long span or extra wide bridges that indicate a basic rate greater than 25 cu. yds. per hr. are to be checked with the Structural Project Manager.
The minimum rate of pour for solid slab or voided slabs is 20 linear feet of bridge per hour and not less than 25 cu. yds. per hour. Check pouring rates with Structural Project Manager if it is indicated necessary to exceed the basic minimum rate of 25 cu. yds. per hour.
The largest minimum rate of pour for alternate pours is 50 cu. yds. per hour in rural areas or 65 cu. yds. per hour in urban areas.
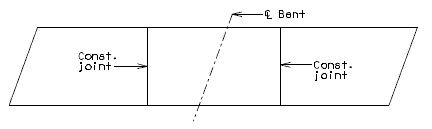
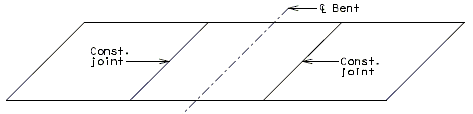
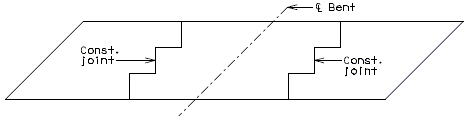
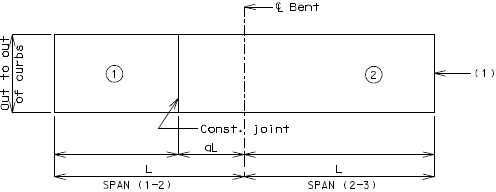
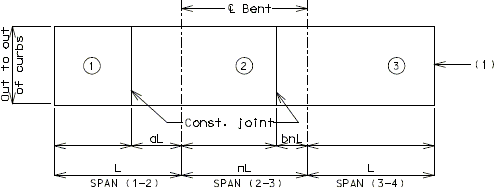
Slab Pouring Sequence Transverse Construction Joints
Slab Pouring Sequence - Bridges on Grade
All bridges on straight grades shall be poured up grade.
All bridges on vertical curves may be poured either up or down grade.
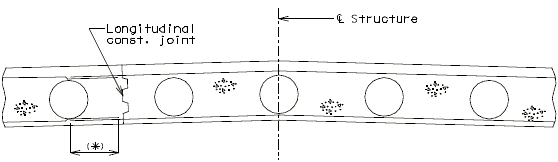
Transverse Construction Joint
On occasion, it will be necessary to off-set the transverse construction joint. For example, on bridges with large skews, wide roadways or short spans, the transverse construction joint could extend across the intermediate bent. Should this occur, the off-set or sawtooth construction joint shall be used.
It is desirable to relocate const. joint within reason (6"±) should it cross additional negative slab reinforcement. However, this shall not be considered critical.
Since the off-set construction joint creates construction problems, the designer shall avoid its use, if possible. Consult the Structural Project Manager for possible variations. See illustrations below for clarification.
Longitudinal Construction Joints
Wide Flange Beam, Plate Girder and Prestressed Girder
Normally, the maximum finishing width is 54'. Larger widths require longitudinal construction joints. Normally, the widest section of slab shall be poured first. During construction, the engineer may opt to eliminate this construction joint. Include note (H6.18) on roadways with longitudinal construction joints to address this option.
The finishing width shall be adjusted to finish the surface approximately parallel to the skew (i.e., skewed transverse construction joints) if the angle of skew exceeds 45° or if the angle of skew exceeds 30° and the ratio of placement width divided by span lengths equals or exceeds 0.8.

|
| Wide Flange Beam or Plate Girder |
|---|
|
| Prestressed Girder |
|
| Voided Slab |
| (*) See Lap Splices of Tension Reinforcement - EPG 751.5 Standard Details |

|

|
| Typical Section thru CIP Slab Construction Joint | Typical Section thru Precast Panel Slab Construction Joint |
|---|
Pouring and Finishing Concrete Roadway Slabs
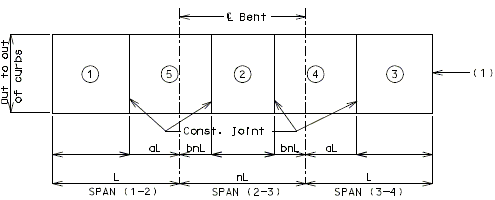
| Span Ratio n | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spans | Coef. | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.25 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 2.0 |
| 2 | a | .4 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 3 | a | .4 | .35 | .30 | .28 | .25 | .22 | .20 | .19 | .18 | .17 | .16 | .15 |
| 3 | b | .15 | .18 | .21 | .25 | .30 | .33 | .35 | .36 | .37 | .38 | .39 | .40 |
| 4 & 5 | a | .4 | .35 | .30 | .28 | .25 | .22 | .20 | .19 | .18 | .17 | .16 | .15 |
| 4 & 5 | b | .15 | .18 | .21 | .25 | .30 | .33 | .35 | .36 | .37 | .38 | .39 | .40 |
| 4 & 5 | c | .15 | .18 | .21 | .25 | .30 | .33 | .35 | .36 | .37 | .38 | .39 | .40 |
Use adjacent spans for ratio n.
Span lengths to be used are center to center of bearing.
Modify the dimensions produced by the coefficients on wide roadways and large skews if they produce construction joints that are within 6" of the additional negative slab reinforcement.
Dimensions, except for terminal lengths of end spans, shall be to the nearest foot.
For 6 & 7 spans, use same coefficients for a, b, & c as for 4 & 5 spans.
PLATE GIRDER AND PRESTRESSED CONCRETE: (2-SPAN)
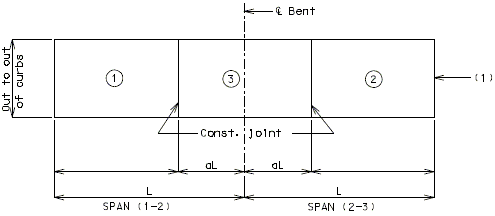
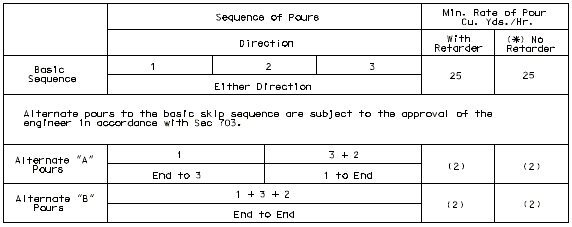
PLATE GIRDER AND PRESTRESSED CONCRETE: (3-SPAN)
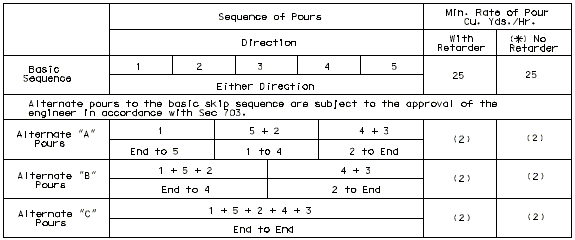
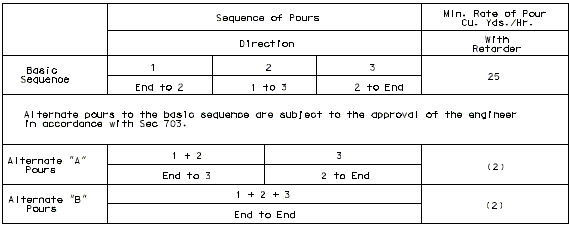
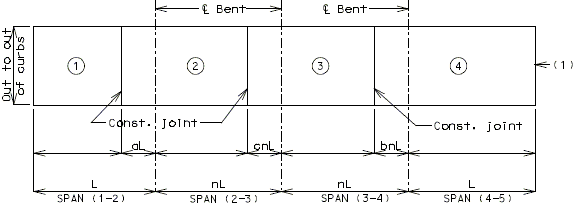
I-BEAM, PLATE GIRDER AND PRESTRESSED CONCRETE: (4-SPAN)
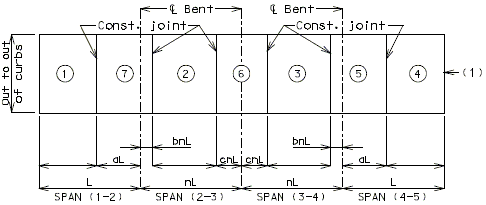
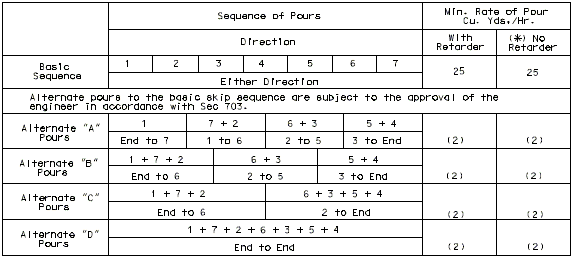
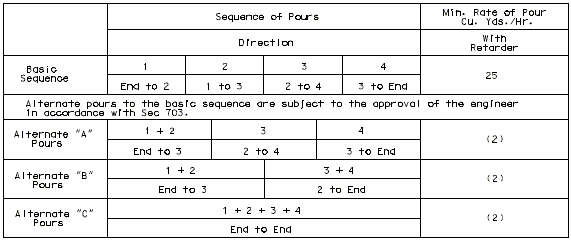
I-BEAM, PLATE GIRDER AND PRESTRESSED CONCRETE: (5-SPAN)
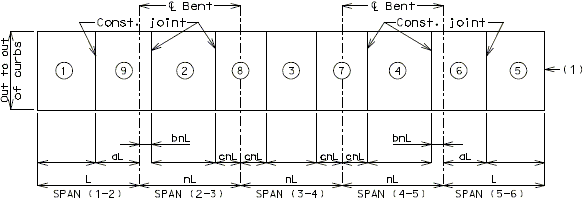
PRESTRESSED CONCRETE: (2-SPAN)
PRESTRESSED CONCRETE: (3-SPAN)
PRESTRESSED CONCRETE: (4-SPAN)
PRESTRESSED CONCRETE: (5-SPAN)
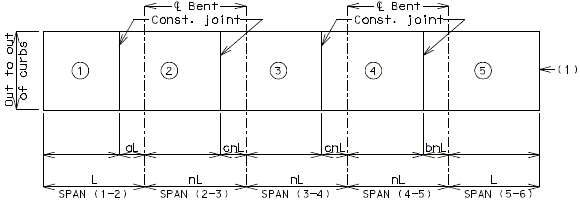
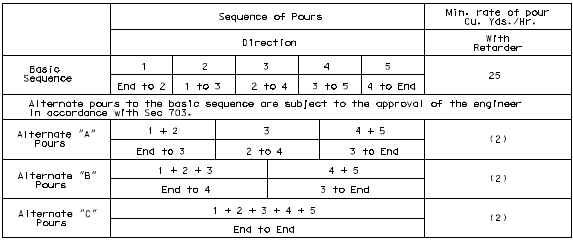
| Note: | Pouring sequence used on prestressed concrete with a basic rate of 25 cu. yds./hr. When multi-series of spans are used - see Structural. Project Manager. Slab pours shown are to be reversed for bridges on a minus grade. |
| (1) | Fill face of end bent or appropriate exposed plates, angles, wide flanges, and joint filler required for expansion devices. Note: For prestressed structures, "aL" and "bnL" may be made shorter than that indicated by the coefficients to balance pours. |
| (2) | Minimum pour rates. |
751.10.1.13 Drip Bevel
Single Drip Bevel

Use a single drip bevel on all standard bridges, the low side of superelevated bridges, the high side of superelevated continuous concrete slab bridges, and at medians.
Double Drip Bevel

Use a double drip bevel on the high side of all superelevated bridges (except continuous concrete slab bridges), and box girder bridges.
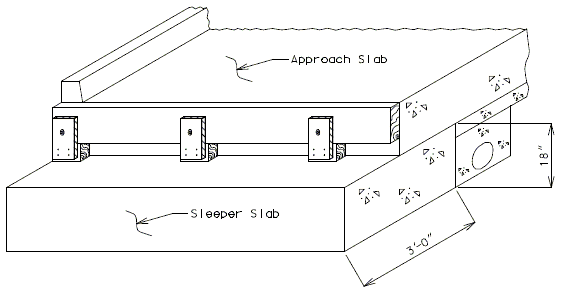
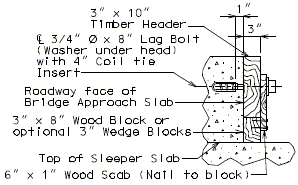
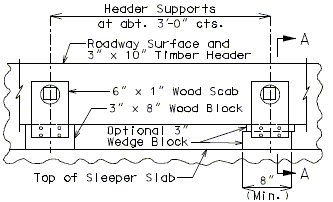
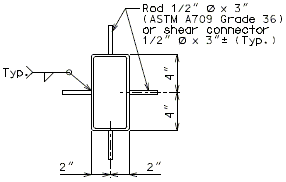
751.10.1.14 Timber Header
751.10.1.15 Deck Concrete Finishing
Bridge decks are normally finished with an approved mechanical finishing machine per Sec 703.3.5. The use of a vibratory screed in place of a finishing machine is allowed if the guidance below is satisfied or the core team determines it is applicable for a particular bridge. Although vibratory screeds may contribute to an overworked concrete surface where durability of the deck may be reduced, there are applications where the weight and bulk of the finishing machine may not be practical. For instance, most re-decks consist of steel wide flange beams where the contractor may have to heavily brace the exterior girders for the finishing machine. Using a vibratory screed may allow the contractor to use less bracing and finish with much lighter equipment. In addition, a vibratory screed is useful when the finishing machine framework is too wide and would interfere with traffic or adjacent physical obstacles. If a vibratory screed is allowed for deck finishing, add note B3.25 (A2.14 for box culverts) on the bridge plans.
Guidance for allowing a vibratory screed:
- (1) Bridges with exterior steel stingers with the web depth 30 in. or less and all the following met:
- Bridge is located on a minor road.
- Bridge width ≤ 32 ft.
- (2) Re-decks on thru trusses with roadway width < 26 ft. and limited horizontal clearance between truss members and edge of deck.
- (3) Bridges with staged pours < 12 ft. and limited available horizontal clearance. Modify note B3.25 to indicate applicable stage(s).
- (4) New box culverts with top slab used as the riding surface.
- (5) Widenings < 12 ft. wide or with limited available horizontal clearance.
751.10.2 Stay-in-Place Bridge Deck Forms
751.10.2.1 Precast Prestressed Concrete Panel Forms - Design
General Guidelines
Precast prestressed concrete panels with 5 ½ in. minimum cast-in-place concrete topping shall be the preferred slab used on all girder structures except as noted in this article.
Precast prestressed panels may be used on horizontally curved steel and concrete structures based upon the approval of the Structural Project Manager or Structural Liaison Engineer. Consideration shall be given to the superelevation magnitude and its effects related to joint filler thickness and width requirements, top flange width requirements for setting panels, increased slab dead load, and any curvature effects on the design and details of the panels related to stability of the panels during a slab pour ensuring that sliding or shifting of the panels isn’t possible and related to cutting of the panels on skew.
- For MoDOT Standard Girders and Steel Girders: Panels shall be set on joint filler in accordance with Sec 1057.6 of Missouri Standard Specifications or polystyrene bedding material. Filler thickness shall be a minimum of 1” and a maximum of 2”. Standard filler width is 1.5” except at splice plates where 3/4” minimum is allowed to clear splice bolts. Joint filler thickness may be reduced to a minimum of 1/4” over splice plates on steel structures. The joint filler thickness may also be varied within these limits to offset girder camber or at the contractor’s option a uniform 1” (min.) thickness may be used throughout. The same thickness shall be used under any one edge of any panel and the maximum change in thickness between adjacent panel shall be 1/4”.
- For NU and MoDOT Bulb Tee Standard Girders: Exceptions are made for NU and MoDOT Bulb Tee Standard Girders, where a maximum joint filler thickness of 4” and a joint filler width that shall be ½” less than the joint filler thickness used but not less than 3” (min.). Increasing the allowable joint filler thickness is necessary to reduce the likelihood of adding steps on long span girders because of camber and to meet minimum haunch and deck cross-slope criteria. Limiting the width of the joint filler to 3” minimum allows for an increased bearing area on the thin flange tips.
As per the above criteria, the following shall control the panel width, measured parallel to the prestressing strands:
- Maximum Panel Width = 9’-6”
- Minimum Panel Width = 4’-0”
Precast prestressed panels shall be used in at least two adjacent bays for each stage of construction. Panels are not designed for simple span (single bay) composite live loading.
When a safety barrier curb or median barrier curb is permanently required on the structure other than at the edge of slab or where precast prestressed panels are not used for other reasons, precast prestressed panels shall not be used in the bay underneath the barrier curb.
Design Stresses
Precast prestressed concrete panels shall be 3” thick with 5.5” cast-in-place concrete slab. Concrete for prestressed panels shall be Class A-1 with = 6.0 ksi and = 4.0 ksi. Cast-in-place portion of slab shall be of strength = 4.0 ksi. The panels are considered as beams for analysis and design.
Prestressing steel shall be AASHTO M 203 (ASTM A 416) – Uncoated Seven-Wire, Low-Relaxation Strands. The strands will be grade 270 ksi, have a nominal diameter of 3/8”, area of 0.085 in.2, and be spaced at 4.5” in the panels.
| = ultimate strength of strands = 270 ksi | |
| = yield strength of strands = 0.9 = 243 ksi | |
| = modulus of elasticity of strands = 28,500 ksi |
Load Definitions
Non-Composite Loading – This is the loading that occurs before the cast-in-place concrete slab hardens and acts compositely with the prestressed panels. The contributions to the Non-Composite Loading are as follows:
- Precast Prestressed Panel, DC
- Cast-In-Place Slab, DC
- Additional Slab Weight due to excess haunch, DC
- Construction Load of 50 lb/ft2
Composite Loading – This is the loading that occurs after the cast-in-place concrete slab hardens and acts compositely with the prestressed panels. The contributions to Composite Loading are as follows:
- Future Wearing Surface, DW
- Safety Barrier Curb, DC
- Design Live Load, LL
Prestress Losses
Refined estimates of time-dependent losses are used, based on LRFD 5.9.5.4, as opposed to approximate lump sum estimate of losses in LRFD 5.9.5.3.
The prestress losses shall be calculated to investigate concrete stresses at two different stages.
- Temporary stresses immediately after transfer:
- Final stresses
Load Combinations for Stress Checks
Note: Units of stress are in ksi.
Construction Loading = DC + 0.050 ksf with Effective Prestressing Force
- Allowable Concrete Tensile Stress =
- Allowable Concrete Compressive Stress =
Service I = Permanent Loads with Effective Prestressing Force
- Allowable Concrete Compressive Stress =
Service I = Live Load + Half the Sum of Permanent Loads and Effective Prestressing Force
- Allowable Concrete Compressive Stress =
Service I = 1.0DC + 1.0DW + 1.0LL with Effective Prestressing Force
- Allowable Concrete Compressive Stress =
Service III = 1.0DC + 1.0DW + 0.8LL with Effective Prestressing Force
- Allowable Concrete Tensile Stress =
Strength I = 1.25*DC + 1.5*DW + 1.75LL with Effective Prestressing Force
- Factored Moment Resistance =
- Where:
- = as calculated in LRFD 5.5.4.2.1
Reinforcement Check
- Minimum Requirement =
751.10.2.2 Precast Prestressed (P/C P/S) Concrete Panel Forms - Details

|

| |
| Panels-Squared Ends | Panels-Skewed Ends | |
|---|---|---|
| PLAN OF PRECAST PRESTRESSED PANELS PLACEMENT | ||
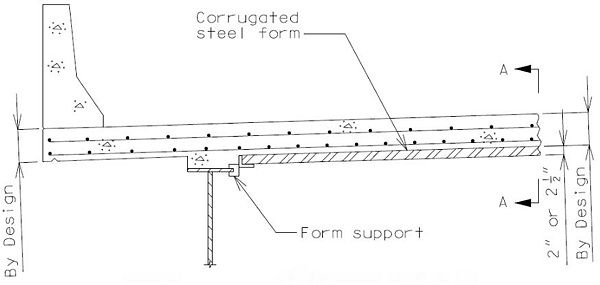
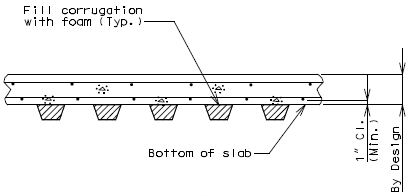
751.10.2.3 Corrugated Steel Forms
General Guidelines
Use of corrugated steel forms may be used on horizontally curved steel structures and prestressed girder, voided slab, and box girder beam structures.
Use of corrugated steel forms shall be based on the approval of the Structural Project Manager or Structural Liaison Engineer.
Use of corrugated steel forms should be based on the final expected conditions of operation and expected in-service performance which should include reviewing the type of crossing, AADT under, salt spray under, surrounding bridge structure conditions, staged construction, etc.
Use of corrugated steel forms should be considered as an alternate method of slab forming where use of precast prestressed concrete panel forms is not practical or not allowed.
Use of corrugated steel forms shall not be considered where precast prestressed concrete panel forms can be used.
Design loading for bridge design shall include an allowance for the dead weight of the steel forms. Use 4 psf dead loading for form spans up to 10 feet beyond which sagging of the form spans and the additional dead weight of the concrete may need to be considered in accordance with LRFD 9.7.4.
Design of corrugated steel forms is the responsibility of the contractor in accordance with Sec 703.
751.10.3 Bridge Deck Drainage - Slab Drains
751.10.3.1 Type, Alignment, Spacing
Type
Slab drains shall be 8" x 4" x 1/4" steel tubing whenever possible.
Alignment
All standard crown roadways shall have the 8" x 4" steel tubing placed with the 8" side perpendicular to the curb whenever possible. All super-elevated roadways shall have the 8" x 4" steel tubing placed with the 8" side parallel to the curb.
Slab Drain Spacing
Slab drain spacing shall be designed according to the 1986 FHWA report "Bridge Deck Drainage Guidelines" along with information acquired from the 1995 University of Missouri Rolla report "Scupper Interception Efficiency." The following general guidelines may be refined if justified by appropriate calculations by other methods of design such as FHWA “HEC 21, Design of Bridge Deck Drainage”. The variations to the design and general requirements listed below should be discussed with the appropriate Liaison or Project Manager on a project by project basis before incorporated into the final design.
General Requirements for Location and Spacing of Slab Drains
- Drains shall be spaced no closer than 8 ft. center to center.
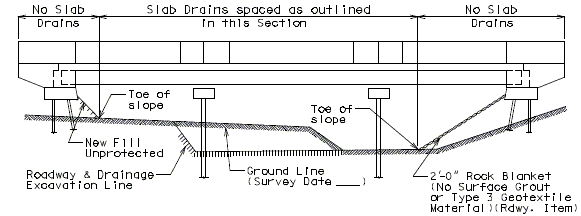
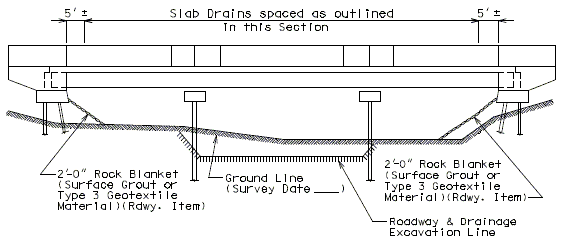
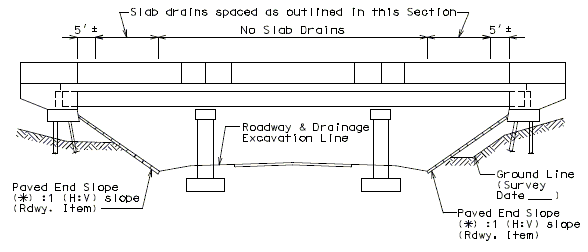
- Drains shall be omitted on high side of super-elevation bridges.
- Drains shall not be located over unprotected fill. If drains are needed, fill should be protected with use of rock blanket with Permanent Erosion Control Geotextile, or concrete slope protection.
- Drains shall be omitted on all grade separations and rail overpasses except when located over concrete slope protection or as noted on Design Layout.
- For Bridges with slopes less than 0.5%, space drains at about 10 ft. centers where possible.
- Use consistent spacing for drains when possible.
- Drains shall be placed at least 5 feet from the face of substructure beam.
- Drains shall be dimensioned along centerline of exterior girder to facilitate placement of coil inserts or holes in girders.
- For all sag vertical curves, locate the points at which the slope is 0.5% on either side of the low point, and space drains on 10 ft. centers between them where possible. Use equations in this section for spacing drains for the remainder of the curve.
- If location restrictions apply, the same number of drains as calculated by equations in this section shall be placed on the bridge when possible. The designer is responsible for relocating drains.
- The length of the approach slab shall be included in the length of the bridge for spacing computations. Do not place slab drains on the approach slab.
Calculation of spacing to first slab drain
The first slab drain either side from the high point of the bridge shall be calculated according the following equation. If the value of L1 is greater than the bridge length, slab drains are not required.
- = Distance from high point to first slab drain (ft.)
- = Cross slope of slab (ft./ft.)
- = Longitudinal slope of bridge (ft./ft.). For vertical curve bridges, "S" is the longitudinal slope at the location of the drain being analyzed. A linear approximation can be used to simplify the calculations.
- = Design spread (ft.). The spread is the width of gutter flow. The spread for any bridge with a 3 ft. or more shoulder width should be taken as 6 ft. If the shoulder width is less than 3 ft., the spread shall be the shoulder width plus 3 ft.
- = Ratio of impervious to pervious drain area. On a bridge deck, most rainfall runs off, except at the beginning of a storm when rain wets the bridge deck and fills small depression areas. Design of slab drain spacing assumes the bridge deck is wetted, therefore a "" value of 1.0 is recommended.
- = Manning's coefficient of friction. For typical pavements, "" equal to 0.016 is used.
- = Design rainfall intensity (in./hr.). The "Rational Method" as outlined in "Hydraulic Engineering Circular-12, (HEC-12)" with a 25 year frequency for a 5 minute time period shall be used to calculate the design rainfall. Missouri's intensity varies from 8.00 in./hr. to 8.50 in./hr. for this frequency and time period. Therefore an "" value of 8.50 in./hr. is recommended to determine slab drain spacing.
- = Width of deck drainage area (ft.). For crowned roadways use distance from top of crown to curb face and for super-elevated bridges use distance from face of curb to face of curb.
Calculation of Additional Slab Drain Spacing
Once the first slab drain has been located, slab drain efficiency "Es" is required to determine the location of additional slab drains. Given the efficiency of the slab drain, the amount of flow intercepted by the first slab drain (q)i is determined by (q)i =Es(QT)i where (QT) is the flow at which the gutter is filled to the design spread (T) at slab drain #1 and is determined by the equation:
- (cu. ft./second)
Interception flow decreases the flow in the gutter by q (intercepted). This flow must be replaced before another slab drain is required. Flow in the gutter at the second slab drain is given by the equation:
- (cu. ft./second)
Another slab drain is located when runoff minus intercepted flow equals flow in the gutter filled to the design spread at length where is the total length of bridge to .
For tangent sections the additional theoretical slab drain spacing are constant. For vertical curve sections the theoretical slab drain spacing are variable and require the designer to repeat the process till the end of the bridge. Theoretical spacing should be revised to consider ease of spacing.
Calculation of Slab Drain Interception Efficiency
Slab drain interception efficiency is that fraction of gutter flow removed by the slab drain. FHWA's report called "Bridge Deck Drainage Guidelines" gives an approximation for for small grates and low gutter velocities, which is a fraction of triangular gutter flow passing over a slab drain located next to the curb.
- = width of slab drain normal to the flow (ft).
- = Design spread.
In UMR's report "Scupper Interception Efficiency" imperical data is used to determine a more precise efficiency coefficient. They state that the slab drain efficiency can be closely approximated by the equation , where is a percent (%) and must be divided by 100 for use in the flow equations.
- = Longitudinal slope of bridge at slab drain location.
- and = Imperical coefficients dependent on the bridge cross-slope. The following tables can be used to determine and .
The UMR method shall be used whenever possible because of its ability to account for increased velocities with increased slopes in its efficiency coefficient. When the design spread "" is other than 6 feet, the FHWA method must be used.
| Cross-Slope | a | b |
|---|---|---|
| 0.010 | 14.580 | -0.180 |
| 0.016 | 6.670 | -0.340 |
| 0.020 | 3.550 | -0.450 |
| 0.030 | 2.080 | -0.500 |
| 0.040 | 2.080 | -0.440 |
| 0.050 | 3.680 | -0.280 |
| 0.060 | 5.510 | -0.140 |
| 0.070 | 4.550 | -0.160 |
| 0.080 | 5.420 | -0.110 |
| Cross-Slope | a | b |
|---|---|---|
| 0.010 | 9.170 | -0.230 |
| 0.016 | 7.060 | -0.280 |
| 0.020 | 5.620 | -0.320 |
| 0.030 | 4.670 | -0.320 |
| 0.040 | 3.060 | -0.370 |
| 0.050 | 3.660 | -0.300 |
| 0.060 | 4.560 | -0.210 |
| 0.070 | 5.500 | -0.130 |
| 0.080 | 5.420 | -0.110 |
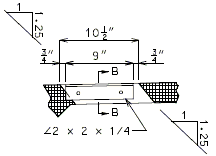
751.10.3.2 Details
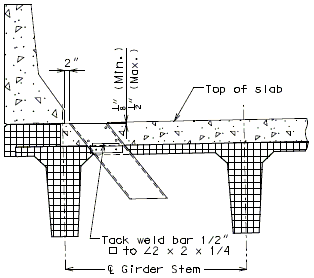
|
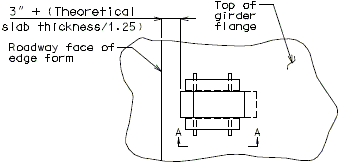
|
| Part Section of Slab at Drain | Part Plan of Drain Blockout |
|---|---|
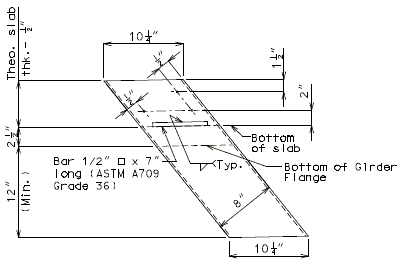
|
|
| Part Section A-A | |
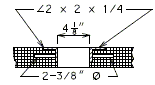
| |
| Elevation of Drain | Section B-B |
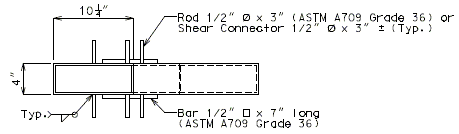
| |
| Plan of Drain | |
751.10.3.3 General Requirements for Location of Slab Drains
751.10.4 Conduit Systems
General
Conduit systems shall be provided on structures when specified on the Design Layout.
All conduits shall be rigid, nonmetallic, schedule 40, heavy wall polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and in accordance with Sec 1060.
All conduit fittings for PVC conduits shall be in accordance with Sec 1060.
All conduit clamps, if required, shall be commercially available, nonmetallic conduit clamps and approved by the engineer.
Drainage shall be provided at low points or other critical locations of all conduits and all junction boxes in accordance with Sec 707. All conduits shall be sloped to drain where possible.
Junction boxes shall be NEMA 4 enclosures and in accordance with Sec 1062.
Deflection couplings at the end of the wings shall be required for probable thermal movements of the structure and ground movements.
Conduit Sizing and Placement Guidelines
Conduit sizes shall be determined realistically and practically by the core team based on the project need and shall be specified on the Design Layout.
Single or multiple conduits may be used.
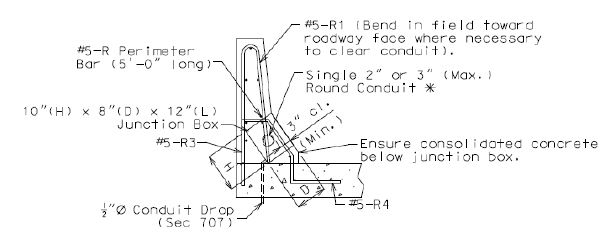
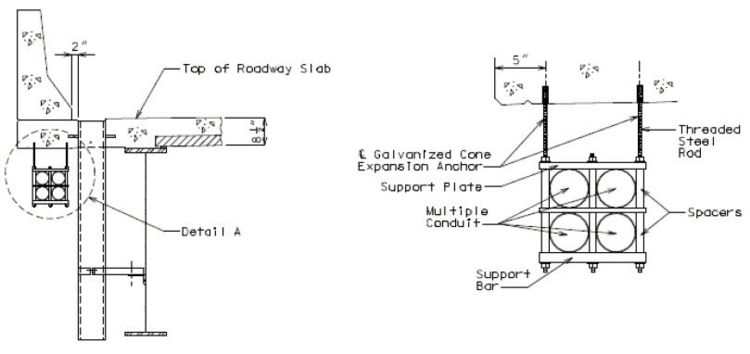
Minimum clearance to single or multiple conduits shall be 3 in., unless otherwise shown.
For single conduit placement, 3 in. round conduit is the maximum size preferred and shall be placed in the safety barrier curb.
- Single 4 in. round conduit may be used based on core team agreement that single 4 in. round conduit is absolutely required to meet the project need. Single 4 in. round conduit shall be placed in the safety barrier curb. (Practical difficulties in placing single 4 in. round conduit in the safety barrier curb could include sweeping from the outside face to the roadway face for junction box connections, increased interference with reinforcement, and less assurance for consolidated concrete under the conduit.)
- Single 2 in. round conduit may be placed in the slab when necessary, for example, when using barrier, either concrete or steel, that cannot accept conduit, or when surplus conduit must be run and placement in the safety barrier curb has been exhausted. Minimum clearance may be less than 3 inches.
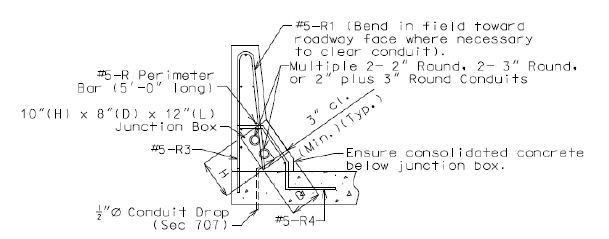
For multiple conduit placement, two 2 in. round conduits, two 3 in. round conduits, or 2 in. plus 3 in. round conduit in combination may be used and shall be placed in the safety barrier curb.
- 4 in. round conduit shall not be combined with 2 in. round conduit or 3 in. round conduit where multiple conduits are to be placed in the safety barrier curb.
- Minimum clearance preferred between conduits placed in the safety barrier curb shall be 1 inch.
- Placement method of multiple conduits shall be determined on a case-by-case basis. Other options include placing conduits on hangers or placing conduits in a deepened slab.
All conduits shall be placed near the outside face of the safety barrier curb. For junction box placements at the roadway face of the safety barrier curb, conduit bends or sweeps shall be required for connecting the conduit to the junction boxes. Refer to Junction Boxes and Placement Guidelines.
Shift reinforcing steel in the field where necessary to clear all conduits and junction boxes.
For placement of single or multiple conduits in barrier curbs other than safety barrier curbs as shown, sizing and placement shall similarly follow these guidelines. Review for applicability and special detailing.
Conduit Systems Placement
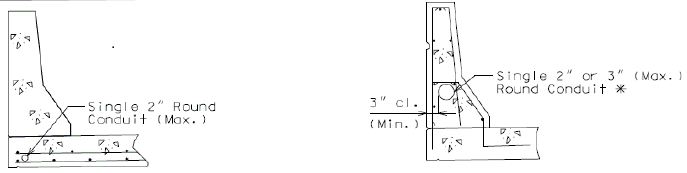
| Section of Single Conduit in Slab | Section of Single Conduit in Safety Barrier Curb | |
| * Single 4 in. round conduit if absolutely required |
 |
 |
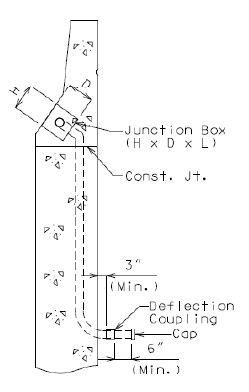
Expansion Fittings and Setting
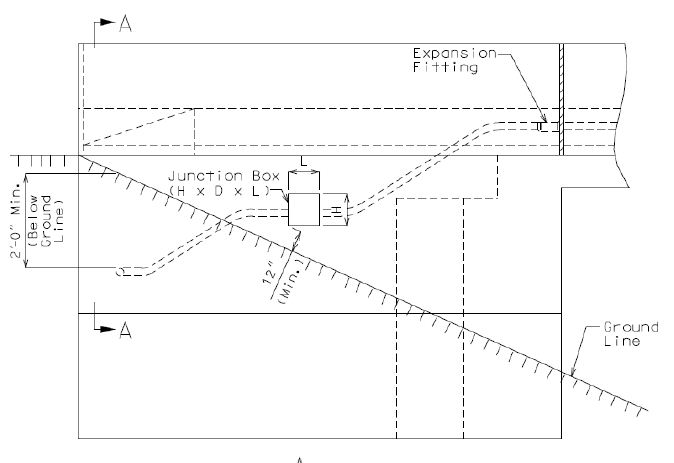
Expansion fittings shall be required where expected bridge movements or conduit movements could cause distress in either conduits or structural supports of conduits.
Bridge movements of primary concern are thermal expansion and contraction, and live load deflections. Both types of movement can occur in structures with or without expansion devices and gaps. Thermal movements are typically predominant.
Conduit movements of primary concern are thermal expansion and contraction. Conduit placed internally to the structure, for example, is encased in concrete, and movement is considered restrained and coincident with the superstructure for which expansion fittings are required only where there is a gap in the concrete. Conduit placed externally to the structure is considered unrestrained for which expansion fittings shall be required.
For expansion fittings of conduit to be encased in concrete:
- Expansion fittings shall be specified on the bridge plans where conduit expansion and contraction will coincide with the expansion and contraction of the bridge superstructure, for example at expansion devices or gaps, i.e. open, closed or filled joints, including filled joints in the barrier curb where conduit is placed in the safety barrier curb.
- Estimated total expansion movement shall be specified on the bridge plans for each location where an expansion fitting is specified and based on the coefficient of thermal expansion for either a steel or concrete superstructure.
- Expansion fittings shall be designed to accommodate a movement of one and a half times the estimated total expansion movement at an open or closed joint, or 4 times the joint filler thickness rounded to the nearest half inch at a filled joint.
- Expansion fittings shall be placed and set in accordance with the manufacturer’s requirements and based on the air temperature at the time of setting given an estimated total expansion movement using a maximum temperature range of 150°F for steel or 120°F if concrete and a maximum temperature of 120°F for steel or 110°F for concrete.
For expansion fittings of conduit not to be encased in concrete:
- Conduit expansion and contraction should be allowed to occur independently of the bridge superstructure movement since the coefficient of thermal expansion for PVC conduit is three times greater than that for steel and concrete.
- The quantity and placement of additional expansion fittings shall be determined by the contractor and in accordance with the conduit manufacturer’s recommendations and specified on the bridge plans except:
- Expansion fittings shall be specified on the bridge plans at all superstructure open, closed or filled joints, and
- Expansion fittings shall be specified on the bridge plans for bridges without open or closed joints near where known conduit restraint will be imposed, for example, where conduits will be rigidly attached at bends or where conduit goes into the ground.
- Estimated total expansion movement shall be specified on the bridge plans for each location where an expansion fitting is specified and based on the thermal movement of PVC conduit for clamped, suspended or conduit otherwise externally supported to or from the superstructure using a coefficient of thermal expansion of 3.38 x 10-5 in./in./°F for PVC conduit.
- Expansion fittings shall be placed and set in accordance with the manufacturer’s requirements based on the air temperature at the time of setting given an estimated total conduit expansion movement using a maximum temperature range of 120°F and a maximum temperature of 110°F. For conduit exposed to direct sunlight, 30°F is added typically to the temperature range for design purposes only.
- Nonmetallic conduit clamps shall be specified to allow the conduit to move freely during expansion and contraction while properly securing it. Expansion fitting barrels should be clamped securely whereas conduit should be mounted loosely so that it can slide freely. Refer to NEMA Standard Expansion Joints for Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Rigid Nonmetallic Conduit. Status: active. Web. 1 January 2010.
- Example 1 – Conduit encased in concrete. Plate Girder superstructure with expansion length of 300 ft.
- Δ (Steel) = (0.0000065)(150)(300)(12) = 3.51 in.
- Δ (Fitting) total = 1.5 x 3.51 = 5.27 in.
- Use 5 1/4 in. total expansion movement.
- Example 2 – Conduit encased in concrete. Expansion at 1/4 in. joint filler in curb.
- Δ (Fitting) total = 4 x 0.25 = 1.0 in.
- Use 1 in. total expansion movement.
- Example 3 – Conduit not encased in concrete and not exposed to direct sunlight. Integral Abutment Bridge with expansion length of 150 ft.
- Δ (Conduit) = (0.0000338)(120)(150)(12) = 7.30 in.
- Δ (Fitting) total = 1.0 x 7.30 = 7.30 in.
- Use 7 1/2 in. total expansion movement for each expansion fitting placed at end of the bridge.
Junction Boxes and Placement
Size and location of junction boxes shall be specified on the bridge plans when a conduit system is required.
Maximum spacing between junction boxes shall be approximately 250 feet.
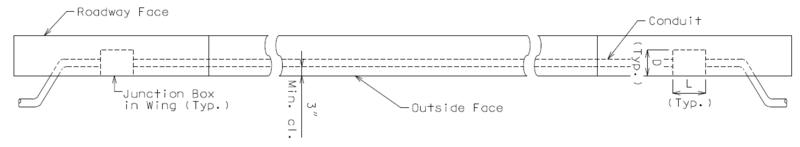
Junction boxes shall be required at each end of the bridge when conduit is required.
All junction boxes shall be placed in the wings at the outside face at each end of the bridge when spacing between the end bent junction boxes is less than 250 ft. and district Traffic does not require an additional junction box on the bridge.
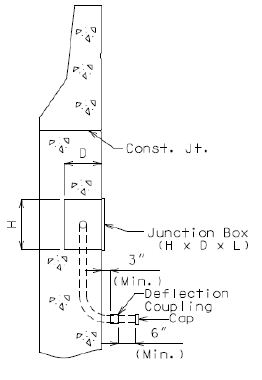
When spacing between the end bent junction boxes exceeds 250 ft., additional junction boxes shall be required and all junction boxes shall be placed in and at the roadway face of the safety barrier curb. (Junction box placement at the roadway face is preferred by Central Office Traffic Division based on simpler accessibility for utility maintenance.)
Placement of junction boxes and covers complete-in-place shall be flush with the roadway face of the safety barrier curb. Junction boxes and covers may be recessed up to 1/4 inch.
Junction boxes should not be placed within 5 ft. of an open, closed or filled joint in the safety barrier curb. Shift reinforcing steel in the field where necessary to clear all junction boxes.
Perimeter steel shall be required at all junction box placements at the roadway face of the safety barrier curb.
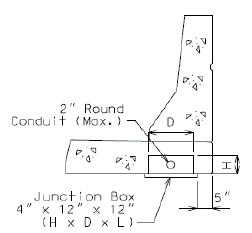
When 2 in. round conduit is placed in the slab, preferred placement of junction boxes shall be in the slab and in areas accessible from underneath the bridge.
| Junction Box Size Requirements | ||
|---|---|---|
| Junction Box Placement | Conduit Design | Junction Box Size |
| H x D x L1, inches | ||
| Safety Barrier Curb or Wing | Single 2” Round Conduit | 10 x 8 x 12 |
| Single 3” Round Conduit | ||
| Single 2” Round Conduit2 | 9 x 9 x 12 | |
| Single 3” Round Conduit2 | ||
| Single 4” Round Conduit | ||
| Two 2” Round Conduit | 10 x 8 x 12 | |
| Two 3” Round Conduit | ||
| 2” plus 3” Round Conduit | ||
| Slab | 2” Round Conduit | 4 x 12 x 12 |
| 1 Length may be increased, if required. Coordinate with core team or district traffic. | ||
| 2 10” x 8” x 12” preferred, but may use 9” x 9” x 12” if cost effective, for example, when used on multiple bridges where required at least once. | ||
Details of Junction Box Placements