Category:170 Maintenance Activity Planning Guidelines: Difference between revisions
m Per Design, added safety logo and info |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[image:safety begins.jpg|165px|center]] | |[[image:safety begins.jpg|165px|center]] | ||
|- | |||
|'''Safety Video''' | |||
|- | |||
|[http://www.youtube.com/user/modotvideo Safety is My Story] | |||
|- | |||
|'''Additional Information''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[http://wwwi/intranet/ri/documents/06-2010.pdf Safe Lifting] | |[http://wwwi/intranet/ri/documents/06-2010.pdf Safe Lifting] | ||
Revision as of 10:57, 21 November 2012

Introduction
 |
| Safety Video |
| Safety is My Story |
| Additional Information |
| Safe Lifting |
The original Maintenance Planning Manual was developed and published in 1989. The purpose of that manual was to provide maintenance managers with a quick reference for performing most maintenance functions. It included scheduling forms, traffic control guidelines, function codes, commodity codes and a sample crew report. While that manual included a substantial amount of useful information, it was never updated or kept current. After that manual was first published, the traffic control for maintenance operations manual was updated into Traffic Control for Field Operations. The function codes and commodity codes have changed because of the financial management system, as well as the crew reporting procedures. In 2003, the 2nd edition of the Maintenance Planning Manual was published to address updates in the industry and to address changes in the MoDOT accounting system.
In 2005 the department set a new direction in how it addresses maintenance and the operation of the state’s roadway system. MoDOT reclassified the department’s thirty-two thousand four hundred miles of roadways into a Major and Minor roadway classification (see map of Major Routes). Major roadways are defined as roadways, which carry 76% of the State’s traffic and totals 5,400 miles. Minor roadways are defined as roadways, which carry 24% of the state’s traffic and totals 27,000 miles.
The Smooth Road Initiative (SRI) was also part of that changes that took place in 2005. SRI targeted 2200 miles of the most heavily used roadways in the Major roadway system for resurfacing, diamond grinding, delineation and guardrail/guardcable improvements.
To address the new direction department management convened a team to identify strategies and best practices that improves MoDOT’s maintenance quality and meets customer expectations. The first deliverable of the team is an update to this Maintenance Planning Guide. The 3rd edition provides the maintenance manager with new and updated planning guidelines by activities and actions. The 3rd edition references other MoDOT publications such as the Traffic Control for Field Operations, Safety Policies, Rules & Regulations-Employee Handbook and the Missouri Standard Specifications for Highway Construction. In addition the 3rd edition includes pictures to illustrate maintenance operations best practices and quality workmanship. Links to referenced publications are also included.
These guides will provide each manager with a list of recommended equipment and materials to use for each function as well as a recommended procedure for that function. The guidelines also have sections on scheduling to help managers plan for the best time of year to do each function and safety reminders on each guideline.
It is intended that this guide be an accurate source of information and a tool that maintenance managers will use to be better organizers, planners and more productive leaders.
Reference the Missouri Standard Plans and Missouri Standard Specifications for Highway Construction for performance details on many of the maintenance function planning guidelines. It is the intent of the department to provide as good of a finished product with Maintenance forces as it does by contract methods.
Recommended materials: When purchasing recommended material, refer to guidance for maintenance materials. Guidance for these materials also refers to the Current General Services Specifications (MGS) by Subject for each of the various maintenance materials.
See also the following reference materials:
- Traffic Control for Field Operations
- Preventive Maintenance Guidelines for Bridges
- Roadside Vegetation Management Guidelines
- Herbicides and Roadsides
- Safety Policies, Rules & Regulations-Employee Handbook
The Highway Maintenance Tables in the appendix were provided to MoDOT through the Local Technical Assistance Program of the Michigan Tech Transportation Institute at Michigan Technological University in Houghton, Michigan.
Rainy Day Activities
| Printable Version |
| Rainy Day Activities |
- Check roadway surface drainage
- Check bridge surface for ponding
- Check bridges and box culverts for drift and erosion
- Flush bridge decks
- Check culverts and culvert pipes
- Check drain basins on bridges
- Check high water locations
- Check, clean and repair equipment
- Clean and repair buildings and grounds
- Blade driveways, entrances, shoulders and mailbox turnouts
- Check signs
- Work on special projects
- Clean abutment caps on bridges
- Cut and treat brush and vines under bridges
- Conduct equipment and safety trainings
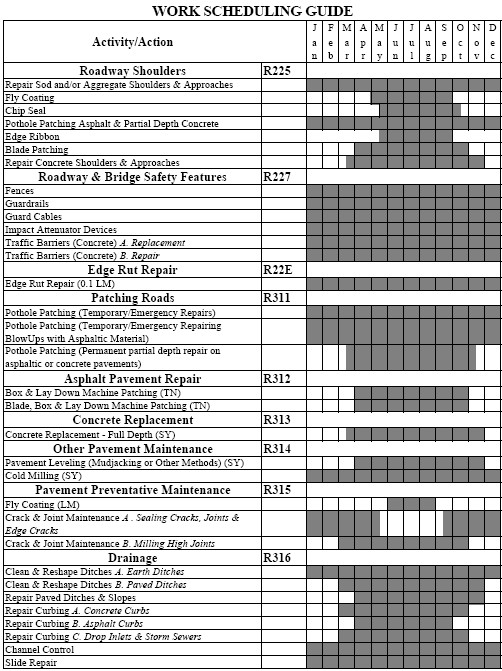
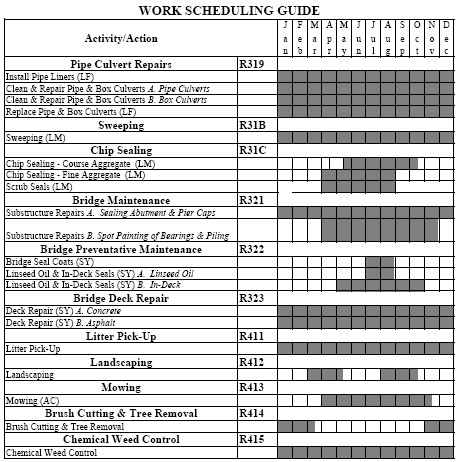
Work Scheduling Guidelines
| Printable Version |
| Work Scheduling Guide |
Index of Printable Planning Guides
Highway Maintenance Tables and Conversion Factors
The Highway Maintenance Tables and Conversion Factors contain helpful tables and conversion factors that aid in volumetric and weight measurements needed in maintenance activities.