Category:940 Access Management: Difference between revisions
m article construction |
m Per TS, updated link to "Managing Access to Missouri's Highways" brochure |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[image:940 access.jpg|center|675px]] | [[image:940 access.jpg|center|675px]] | ||
| Line 12: | Line 7: | ||
In order to be successful in managing access, MoDOT must work to gain the cooperation and support of affected communities, business owners, and the public. Flexibility, good judgment, negotiation and compromise will be necessary to determine the right solution for each location. | In order to be successful in managing access, MoDOT must work to gain the cooperation and support of affected communities, business owners, and the public. Flexibility, good judgment, negotiation and compromise will be necessary to determine the right solution for each location. | ||
{|style="padding: 0.3em; margin-right:10px; border:2px solid #a9a9a9; text-align:center; font-size: 95%; background:#f5f5f5" width="250px" align="left" | |||
|- | |||
|'''Additional Resources''' | |||
|- | |||
|[http://teachamerica.com/cve/ Corridor Visualization Explorer], a high-level planning tool for managing corridors | |||
|- | |||
|[https://www.modot.org/media/31627 MHTC Policy about Limited Access Roadways - Delegation of Authority] | |||
|- | |||
|[https://www.modot.org/media/31628 MHTC Policy about Limited Access Roadways – Execution of Documents] | |||
|- | |||
|colspan="2"|'''Additional Information''' | |||
|- | |||
|[https://modotgov.sharepoint.com/sites/ts/Access%20Management/Forms/AllItems.aspx?id=%2Fsites%2Fts%2FAccess%20Management%2FMoving%20Right%20Along%20%2D%20Managing%20Access%20To%20Missouri%20Highways%2Epdf&parent=%2Fsites%2Fts%2FAccess%20Management Managing Access to Missouri's Highways] | |||
|} | |||
Access management is the proper planning and design of access to the public roadway system that helps ensure traffic flow more smoothly, with fewer crashes, which means everyone travels safer. Access management guidelines include proper spacing of interchanges, public road intersections, traffic signals and driveways. | |||
[[image:940 How MoDOT manages.jpg|right|250px]] | |||
Successful access management also involves a partnership between MoDOT and local land use planning officials. Districts are to establish mutually beneficial and cooperative relationships with city and county stakeholders. Local governments can help MoDOT manage on-site issues that influence the operation of our roadway, but occur beyond the MoDOT right of way. | Successful access management also involves a partnership between MoDOT and local land use planning officials. Districts are to establish mutually beneficial and cooperative relationships with city and county stakeholders. Local governments can help MoDOT manage on-site issues that influence the operation of our roadway, but occur beyond the MoDOT right of way. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 30: | ||
Decisions regarding the spacing and design of interchanges, public road intersections and driveways must reflect a balance of access to homes and businesses with sound traffic engineering principles. Decision points could include: | Decisions regarding the spacing and design of interchanges, public road intersections and driveways must reflect a balance of access to homes and businesses with sound traffic engineering principles. Decision points could include: | ||
:* [[940.2 Spacing between Interchanges|spacing between interchanges]] | |||
:* [[940.3 Clearance of Functional Areas of Interchanges|clearance of functional areas for interchanges]] | |||
:* [[940.5 At Grade Intersections Spacing| at grade intersections spacing]] | |||
:* [[940.6 Traffic Signal Spacing|traffic signal spacing]] | |||
:* [[940.13 Driveway Spacing|driveway spacing]] and density | |||
:* [[940.14 Driveway Corner Clearance|driveway corner clearance]] | |||
:* [[940.8 Raised Medians|raised medians]] | |||
:* [[940.15 Spacing and Clearance for Right-In, Right-Out Driveways|spacing and clearance for right-in, right-out driveways]] | |||
:* [[Functional Intersection Area|clearance of functional areas of public road intersections]] | |||
:* [[:Category:941 Permits and Access Requests#941.7 Sight Distance for Entrances|sight distance]] | |||
:* [[940.16 Driveway Geometrics|driveway geometrics]] | |||
:* [[940.10 Two-Way Left-Turn Lanes ("Five-Lane" Facilities)|two-way left-turn lanes (“five-lane” facilities)]] | |||
:* [[940.12 Frontage and Backage Roads|frontage and backage roads]] | |||
[[image:940 speed.jpg|left| | [[image:940 speed.jpg|left|175px]] | ||
Routes classified as interstate/freeway are intended to carry long-distance, higher-speed travel and will have a high level of access control. Interchanges are to be spaced to allow smooth and safe flow of traffic entering and exiting the freeway. Generally, speeds are higher in rural areas, so interchanges must be spaced farther apart there than in urban areas. | Routes classified as interstate/freeway are intended to carry long-distance, higher-speed travel and will have a high level of access control. Interchanges are to be spaced to allow smooth and safe flow of traffic entering and exiting the freeway. Generally, speeds are higher in rural areas, so interchanges must be spaced farther apart there than in urban areas. | ||
All interchange spacing decisions are to be supported by operation and Level of Service studies. Connectivity with the local street system, speed and safety will also be considered. | All interchange spacing decisions are to be supported by operation and [[902.12 Glossary#Level of Service (LOS)|Level of Service]] studies. Connectivity with the local street system, speed and safety will also be considered. | ||
[[image:940 Access Management Advantages.jpg|560px|right|thumb|<center>'''Access Management Advantages'''</center>]] | |||
In major freeway routes, the spacing of the outer road from the ramp must allow traffic adequate room to exit the ramp, ([[940.4 Freeway and Expressway Transition|freeway and expressway transition]]), without negatively impacting the operation of the interchange and freeway. | In major freeway routes, the spacing of the outer road from the ramp must allow traffic adequate room to exit the ramp, ([[940.4 Freeway and Expressway Transition|freeway and expressway transition]]), without negatively impacting the operation of the interchange and freeway. | ||
Latest revision as of 11:17, 5 April 2022

Roadways must provide efficient and safe access to homes and businesses. This concept is the foundation of any successful access management effort. Economic prosperity for businesses of all sizes is dependent upon the appropriate level of access and is an important consideration in determining where access should be restricted and/or limited.
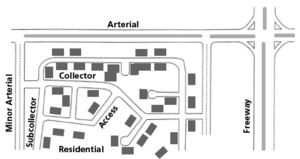
Local and lower-volume routes provide access to homes and businesses while higher-volume arterial routes like interstates and major highways are needed to serve longer, higher-speed travel. The more traffic on a roadway, the more essential access management becomes. Properly managed access provides access to homes and businesses while still improving roadway safety and traffic operations and protecting the taxpayers’ investment in roadways.
In order to be successful in managing access, MoDOT must work to gain the cooperation and support of affected communities, business owners, and the public. Flexibility, good judgment, negotiation and compromise will be necessary to determine the right solution for each location.
| Additional Resources | |
| Corridor Visualization Explorer, a high-level planning tool for managing corridors | |
| MHTC Policy about Limited Access Roadways - Delegation of Authority | |
| MHTC Policy about Limited Access Roadways – Execution of Documents | |
| Additional Information | |
| Managing Access to Missouri's Highways | |
Access management is the proper planning and design of access to the public roadway system that helps ensure traffic flow more smoothly, with fewer crashes, which means everyone travels safer. Access management guidelines include proper spacing of interchanges, public road intersections, traffic signals and driveways.

Successful access management also involves a partnership between MoDOT and local land use planning officials. Districts are to establish mutually beneficial and cooperative relationships with city and county stakeholders. Local governments can help MoDOT manage on-site issues that influence the operation of our roadway, but occur beyond the MoDOT right of way.
Roadways serve dual purposes of providing both efficient movement of traffic and access to adjacent property. A higher level of access management is necessary on major roads so that traffic can move safely and efficiently. Many minor roads may also warrant some level of management. However the techniques used are to provide an appropriate balance between the through movement and the need to access the adjacent properties. At a minimum, it is important to maintain adequate sight distance.
Decisions regarding the spacing and design of interchanges, public road intersections and driveways must reflect a balance of access to homes and businesses with sound traffic engineering principles. Decision points could include:
- driveway spacing and density

Routes classified as interstate/freeway are intended to carry long-distance, higher-speed travel and will have a high level of access control. Interchanges are to be spaced to allow smooth and safe flow of traffic entering and exiting the freeway. Generally, speeds are higher in rural areas, so interchanges must be spaced farther apart there than in urban areas.
All interchange spacing decisions are to be supported by operation and Level of Service studies. Connectivity with the local street system, speed and safety will also be considered.

In major freeway routes, the spacing of the outer road from the ramp must allow traffic adequate room to exit the ramp, (freeway and expressway transition), without negatively impacting the operation of the interchange and freeway.
On major non-freeway routes, median opening spacing, public road intersections and traffic signals are important considerations in managing access.
Routes classified as minor arterials and collectors make up the bulk of MoDOT’s system, serve more local destination traffic and have a lower level of access control.
This article also includes discussions of parking on facilities, retrofit and permit applications, three-lane cross-sections and auxiliary acceleration and turning lanes.
Articles in "940 Access Management"
The following 17 pages are in this category, out of 17 total.
9
- 940.1 Analysis of Retrofit and Permit Applications
- 940.2 Spacing between Interchanges
- 940.3 Clearance of Functional Areas of Interchanges
- 940.4 Freeway and Expressway Transition
- 940.5 At Grade Intersections Spacing
- 940.6 Traffic Signal Spacing
- 940.7 Median Opening Spacing
- 940.8 Raised Medians
- 940.9 Auxiliary Acceleration and Turning Lanes
- 940.10 Two-Way Left-Turn Lanes ("Five-Lane" Facilities)
- 940.11 Three-Lane Cross-Sections
- 940.12 Frontage and Backage Roads
- 940.13 Driveway Spacing
- 940.14 Driveway Corner Clearance
- 940.15 Spacing and Clearance for Right-In, Right-Out Driveways
- 940.16 Driveway Geometrics
- 940.17 Parking on Facilities